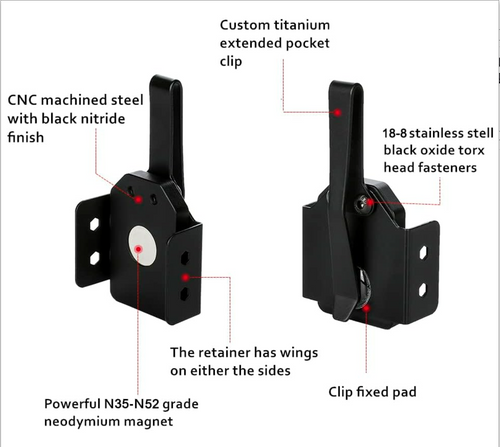
Trigger guard retention systems are designed to secure your firearm while allowing quick access when needed. Here's a quick breakdown:
- Passive Retention: Uses friction to hold the firearm in place. It's simple, fast, and requires no extra action to draw but may loosen over time.
- Active Retention: Includes mechanical locks like thumb breaks or button releases. It offers higher security but requires extra steps and training for a smooth draw.
Quick Comparison
| Feature | Passive Retention | Active Retention |
|---|---|---|
| How It Works | Friction and tension | Mechanical release mechanisms |
| Draw Speed | Fast and simple | Slower, requires extra steps |
| Security | Basic firearm hold | High with locking mechanisms |
| Training Need | Minimal | Requires consistent practice |
| Best For | Everyday concealed carry | High-risk or active scenarios |
Choose a retention system based on your activity level, environment, and training. Regular practice ensures you can draw safely and efficiently when it matters most.
Practical Guide to Gun Holsters
What Is Trigger Guard Retention
Trigger guard retention refers to the system in a holster or trigger guard cover that keeps a firearm secure until the user intentionally draws it. These systems are designed to prevent accidental dislodgment while still allowing for a quick and smooth draw.
Understanding Retention Basics
Retention systems aim to balance firearm security and accessibility, especially for concealed carry. A good system creates enough friction to hold the firearm securely but still allows for easy access when needed. At Houdini Holsters, this balance is achieved through precise contact points and carefully selected materials.
These principles form the foundation for the two main types of retention systems.
Types of Retention Systems
Retention systems generally fall into two categories: passive and active.
| Retention Type | How It Works | Interaction Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Passive | Uses friction and tension | None |
| Active | Includes a mechanical release | Requires a release action |
Passive retention relies on friction between the holster material and the firearm. This option is often preferred for concealed carry since it prioritizes quick access.
Active retention adds a mechanical element that must be released before drawing the firearm.
Choosing the right retention system comes down to finding the right balance between secure hold and quick accessibility for your specific needs.
Passive Retention Systems
Passive Retention Mechanics
Passive retention systems use friction and material design to keep firearms securely in place. These systems rely on precisely molded materials that fit specific firearm models. For instance, the Breakout 2.0 IWB holster by Houdini Holsters uses well-placed contact points to create enough tension for secure retention.
Key features include:
- Material tension: The holster material applies consistent pressure against the firearm.
- Contact points: Specific areas of the holster grip the firearm for added security.
- Friction coefficient: The resistance between the holster and firearm ensures stability.
These elements work together to secure the firearm while also shaping the holster's usability in real-world situations. The design directly impacts performance, balancing ease of use with reliability.
Passive Retention Benefits and Limits
Passive retention systems come with their own set of pros and cons for concealed carry. Here's a detailed look:
| Aspect | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Draw Speed | Quick and efficient deployment | May loosen over time with regular use |
| Maintenance | Requires little upkeep | Tension may need occasional adjustment |
| Reliability | No mechanical components to fail | Retention can be affected by weather |
| Training | Easy to use with minimal training | Proper holster positioning is essential |
| Security | Sufficient for daily carry | Less secure compared to active retention systems |
The system works best when the holster is properly maintained and positioned. It offers a good balance of accessibility and security, making it ideal for situations where quick access is important. However, users should regularly inspect the holster to ensure it maintains consistent tension, especially after heavy use or exposure to different weather conditions.
A high-quality passive retention holster is designed to stay secure during everyday movements while preventing the firearm from shifting or dislodging. Routine checks and adjustments help ensure reliability over time.
Active Retention Systems
How Active Retention Works
Active retention systems use mechanical devices that require deliberate actions to release a firearm. Unlike passive systems that depend on friction, these systems demand intentional engagement to ensure the weapon is securely held until needed.
Common components of active retention systems include:
- Thumb breaks: Straps or levers that must be pressed down or forward
- Button releases: Mechanisms triggered by finger pressure
- Hood guards: Covers that must be moved aside before accessing the firearm
- Multi-point locks: Systems requiring a sequence of actions to unlock
While these features improve security, they also introduce steps that can affect draw speed, creating a purposeful safeguard against accidental release.
Pros and Cons of Active Retention
Active retention systems come with both advantages and challenges, depending on their use.
| Feature | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Increased protection with locking mechanisms | Draw Speed: Additional steps may slow access |
To use these systems effectively, consistent training is essential. Users need to:
- Practice the release mechanics regularly
- Maintain proficiency through ongoing drills
- Test their skills in varied conditions and scenarios
For law enforcement or high-risk environments where weapon security is critical, these systems add an important layer of protection. However, the trade-off between security and quick accessibility is a key consideration when selecting the right system.
sbb-itb-7fb5bb8
Retention Level Guide
Choose a retention level that matches your daily activities, training experience, and the environments you navigate. It's important to ensure your holster provides both security and accessibility based on your specific needs.
Key factors to weigh include:
- Your daily routine and typical environments: Are you in high-activity or low-risk areas?
- Your training and draw skills: How comfortable and efficient are you under pressure?
- Potential risks you might face: What level of security do you need to feel prepared?
Keep in mind, holsters with added retention features often require more practice to master a smooth, quick draw.
Houdini Holsters specializes in custom handmade designs that prioritize comfort, concealment, and quick access. Use these points to help you select the right retention system in the following section.
Picking the Right Retention System
Selection Factors
When choosing a retention system, think about your daily activities and how you plan to use it. Here's a quick comparison to help you decide:
| Factor | Passive Retention | Active Retention |
|---|---|---|
| Activity Level | Best for low to moderate activity | Suited for high-activity situations |
| Draw Speed | Fast and simple access | Requires extra steps |
| Security Level | Basic protection | Offers added security features |
| Training Need | Little practice needed | Requires more in-depth training |
| Environment | Works well in controlled settings | Suitable for high-risk or public areas |
A great example is Houdini Holsters' Breakout 2.0, which strikes a balance for everyday use. Once you've matched your retention system to your needs, the next step is dedicated training to ensure you're ready for real-world use.
Training Requirements
To get the most out of your retention system, consistent practice is key. Here's how to build your skills:
- Dry-fire practice: Spend 15–20 minutes daily practicing your draw.
- Active release techniques: Repeat these until they become second nature.
- Consistency: Use the same draw techniques during all sessions.
For active retention systems, specifically, focus on:
- Developing muscle memory for smooth operation.
- Keeping a secure grip while releasing the mechanism.
- Practicing your draw from different positions.
The goal is to create reliable, repeatable movements that work under pressure. With regular training, you'll be prepared to access your firearm quickly and safely when the situation demands it.
Conclusion
Trigger guard retention systems play a key role in firearm security and draw speed, striking a balance between friction-based simplicity and mechanical locking mechanisms. Passive retention relies on friction for straightforward security, while active retention adds an extra layer of protection with mechanical locks.
Your choice should align with your specific needs and circumstances. For example, if you operate in a controlled environment, passive retention might be enough. On the other hand, roles involving high activity or public exposure often benefit from the added security of active retention systems.
The Breakout 2.0 IWB holster from Houdini Holsters is a great example of a design that blends secure retention with quick access. Made in the USA and backed by a lifetime guarantee, it’s built to perform when you need it most.
Regular practice is essential to ensure you can draw your firearm both quickly and safely. Choose a retention system that fits your environment and training level to maintain the right mix of security and accessibility.
FAQs
What’s the difference between passive and active retention systems, and how do I choose the right one?
Passive and active retention systems serve different purposes when it comes to trigger guard covers, so choosing the right one depends on your specific needs.
Passive retention relies on friction or pressure to hold your firearm in place. It’s simple, quiet, and ideal for everyday carry or situations where quick, silent access is key. Active retention, on the other hand, uses a locking mechanism that must be manually released to draw the firearm. This provides extra security, making it a great choice for activities where your firearm might be jostled or for added peace of mind.
When deciding, consider your priorities: If speed and ease of access are most important, passive retention might be the way to go. If you need maximum security, active retention could be a better fit.
How can I keep my passive retention holster working effectively over time?
To maintain the effectiveness of a passive retention holster, regular care is essential. Clean the holster periodically to remove dirt, dust, and debris that could interfere with the retention mechanism. Use a soft, damp cloth for cleaning and avoid harsh chemicals that might damage the material.
Inspect your holster regularly for signs of wear, such as cracks or deformities, especially around the trigger guard area. If you notice significant wear, consider replacing the holster to ensure safe and reliable retention.
Lastly, if your holster is adjustable, periodically check and tighten any screws or retention settings to maintain the desired level of hold for your firearm.
What’s the best way to practice for a smooth and fast draw with an active retention system?
To master a smooth and quick draw with an active retention system, consistent practice is key. Start by familiarizing yourself with the specific retention mechanism on your holster. Practice disengaging the retention feature repeatedly until it becomes second nature.
Once you’re comfortable, incorporate drawing drills into your training routine. Use an unloaded firearm and practice drawing from your holster slowly at first, focusing on proper hand placement and fluid motion. Gradually increase your speed as your confidence and muscle memory improve. For added realism, consider using a timer to simulate high-pressure scenarios. Remember, safety always comes first - double-check that your firearm is unloaded before practicing.